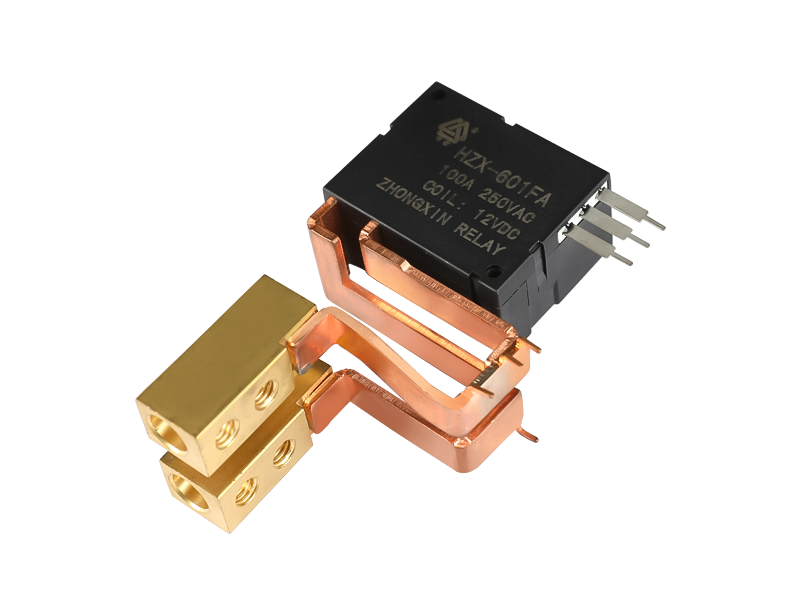
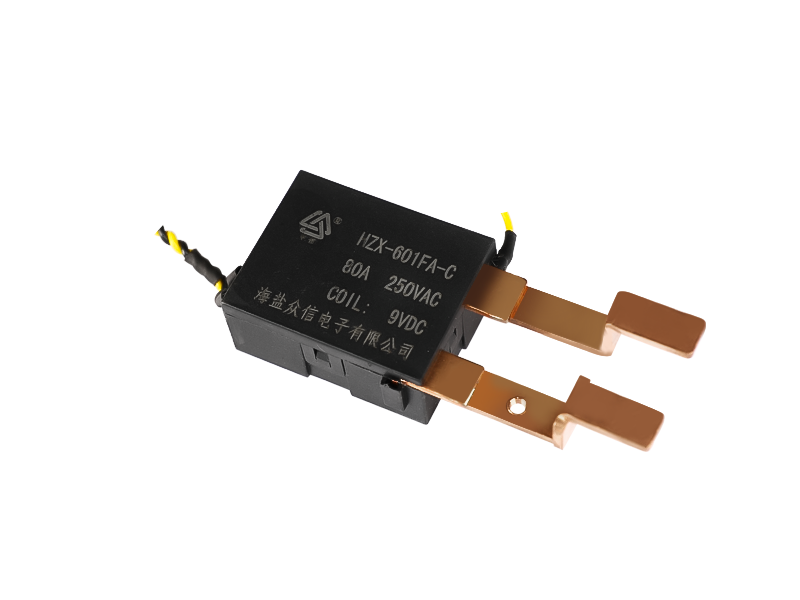
A
latching relay is a type of electrical switch that has a remanent core that holds the contacts in their operating positions. To release them, they need a pulse of the opposite polarity. A permanent magnet in a latching relay closes the contacts. A coil provides force to move the contacts. The coil can either help or oppose the magnetic field. When a pulse is supplied to one coil, the relay is switched on and the opposite coil turns it off.
A latching relay operates in a similar manner to a two-position toggle switch. The handle is physically pushed to one position and remains there until pressed to the opposite position. The latching relay's electrical state is set to a single position until reset. A latching relay's schematic wiring diagram shows how the electronic parts interact with one another to perform the basic memory function. There are a variety of applications for this type of switch, including the control of electrical currents and lighting.
The transistors are connected to the positive and negative terminals of a latching relay. An NPN transistor's base is connected to a positive voltage, while a PNP transistor's base is grounded. The transistor BC547's base conducts when the base of the transistor is grounded. When this happens, the transistor is turned on. The relay turns on the connected device. However, the positive voltage can also be applied to the other end of the relay.
The circuit current pushes a magnet-covered reed switch between two coils. The magnetic pulse pushes the switch from one side to the other, while the opposite magnetic pulse pushes the switch back to the opposite terminal. When the current is turned off, the latching relay remains in its last position. It is possible to reset the latching relay using a different switch, which is shown on the schematic. This method will enable you to use a latching relay in a wide variety of applications.
Besides the magnetic coils, latching relays are made of a solid-state circuit and a mechanical mechanism. These relays use locking mechanisms to determine the position of the contacts. When power is applied to one coil, the other is energized and the contacts remain locked until the opposite coil receives energy. The cycle repeats. This mechanism is highly effective for controlling power systems.
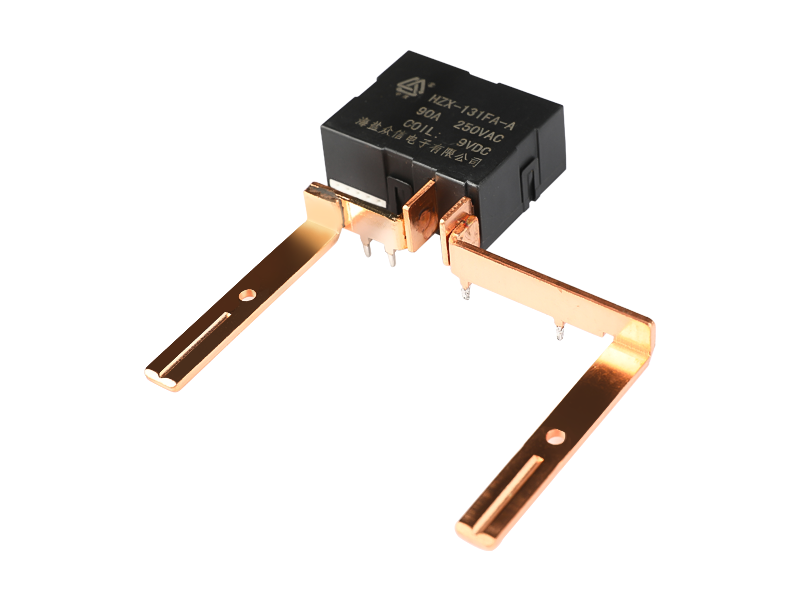
-
- 90A switching capability
- Very minimal power consumption from the coil
- 9mm creepage distance
- 4KV dielectrics strength coil to contact
- In accordance with IEC62055-31:UC2
- Outline dimensions:(36*30*16.5)mm
- CE,CQC compliant
- RoHS,UL compliant
Type: Magnetic Latching Relays
Theory: Electromagnetic Relay
Usage: Household Appliances Relay, General Purpose
Protective Characteristics: Sealed Relay
Action Principle: Electromagnetic Type



 English
English