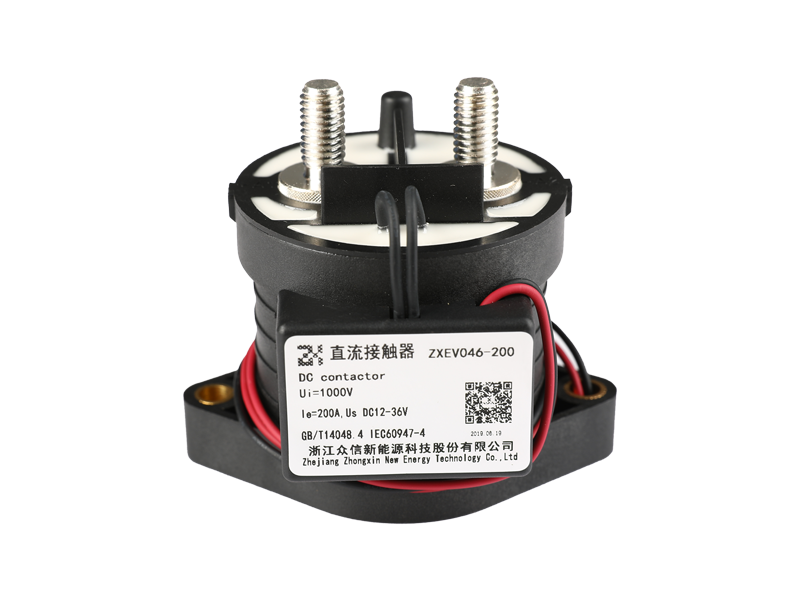
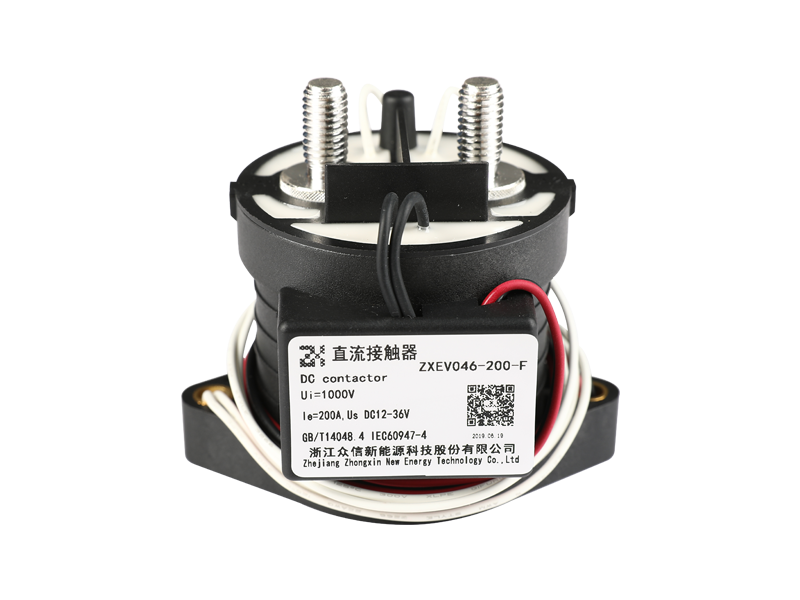
In the rapidly evolving landscape of power electronics and energy systems, the demand for reliable, compact, and durable switching devices continues to escalate. Among the numerous solutions available, the ceramic high voltage direct current relay has emerged as a critical component in advanced electrical infrastructure. Its performance is not only defined by its switching capacity but also by its unique insulation properties, which ensure operational safety and system longevity.
High voltage direct current (HVDC) applications inherently involve the transfer of large amounts of energy under demanding electrical conditions. In such an environment, even the slightest compromise in insulation can dielectric breakdown, arc formation, or leakage currents, each posing significant risks to system performance and safety.
The insulation within a ceramic high voltage direct current relay serves as the primary barrier between conductive parts and external surroundings. Unlike conventional materials, ceramic insulation provides a unique combination of high dielectric strength, low leakage current, and thermal stability. This ensures that relays can withstand voltage stresses consistently over long operational lifecycles.
The use of ceramic in high voltage relays is not coincidental. Ceramics inherently offer exceptional dielectric properties that outperform many polymer-based alternatives. Their ability to maintain high insulation resistance even under conditions of elevated temperature, humidity, and voltage spikes provides relays with a critical edge.
Moreover, ceramic materials are resistant to aging, thermal fatigue, and chemical degradation, making them particularly well-suited for industrial, automotive, and renewable energy environments where reliability cannot be compromised. When integrated into ceramic high voltage DC relays, these properties translate into longer product lifespans and reduced maintenance cycles.
The significant challenges in HVDC relay design is arc suppression. Direct current arcs are difficult to extinguish once initiated, as DC lacks the natural zero-crossing point of AC. Poor insulation can accelerate arc formation and compromise system safety.
Here, ceramic insulation acts as a protective shield, preventing conductive paths from forming even under high stress. Combined with optimized relay geometry, this insulation enables arc suppression ceramic relay designs that maintain stability during switching events, thereby protecting surrounding components from electrical damage.
As industries move towards renewable energy integration, electric vehicles, and large-scale battery storage, insulation performance in relays becomes even more critical. Applications such as:
In each of these cases, insulation not only supports safe switching but also contributes to system efficiency, thermal stability, and reduced risk of catastrophic failure.
With ongoing innovation in power systems, there is a growing demand for smaller, lighter, yet more powerful relays. However, miniaturization increases the risk of insulation breakdown, as the clearance between conductive paths is reduced.
Ceramic insulation provides the necessary high dielectric strength in compact geometries, enabling the design of small form-factor relays without compromising safety. This allows manufacturers to deliver compact ceramic HVDC relay solutions suitable for next-generation automotive, aerospace, and grid systems.
Another advantage of strong insulation lies in its impact on operational longevity. Relays with robust ceramic insulation resist electrical aging caused by prolonged exposure to voltage stress. This translates into:
For industries relying on uninterrupted power supply, such as data centers or transportation infrastructure, the reliability of ceramic high voltage direct current relays becomes a decisive factor in overall system performance.
Looking ahead, insulation performance will remain a defining benchmark for relay innovation. As regulatory frameworks tighten around safety, efficiency, and sustainability, the industry will increasingly measure relay quality by insulation resistance, dielectric strength, and arc suppression capability.
The ceramic encapsulated high voltage DC relay is thus positioned as a central technology in advancing global energy transition goals. Its insulation characteristics directly align with the requirements of green energy systems, electrified transportation, and digital infrastructure.
The ceramic high voltage direct current relay represents far more than a simple switching device; it is a safeguard for modern electrical systems. Its outstanding insulation performance not only ensures safety and reliability but also enables innovation in compact design, renewable energy integration, and high-efficiency power distribution.
As industries pursue higher voltages, greater power densities, and cleaner energy sources, ceramic insulation will remain the cornerstone of HVDC relay technology. The evolution of these devices is ultimately tied to how effectively insulation can meet the challenges of a rapidly electrifying world, making it the defining feature of the relay’s future.