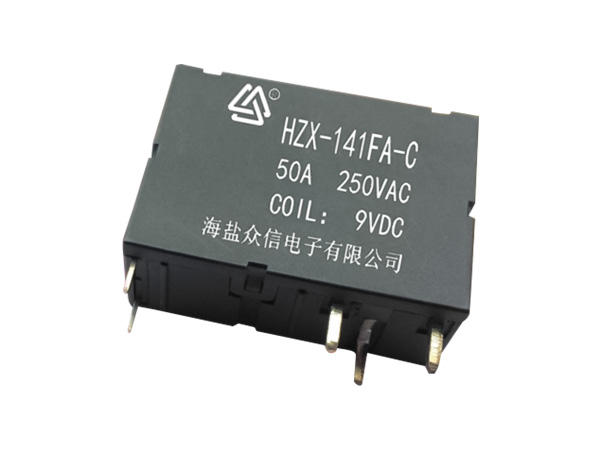
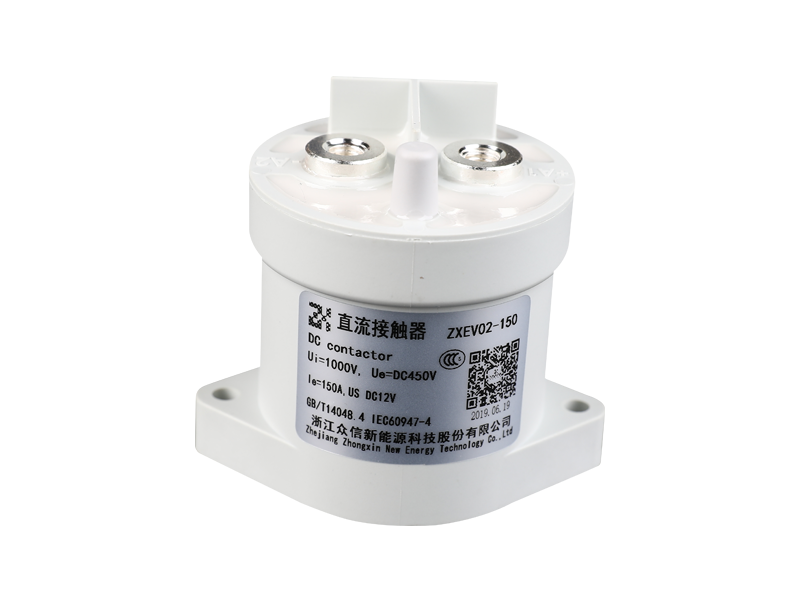
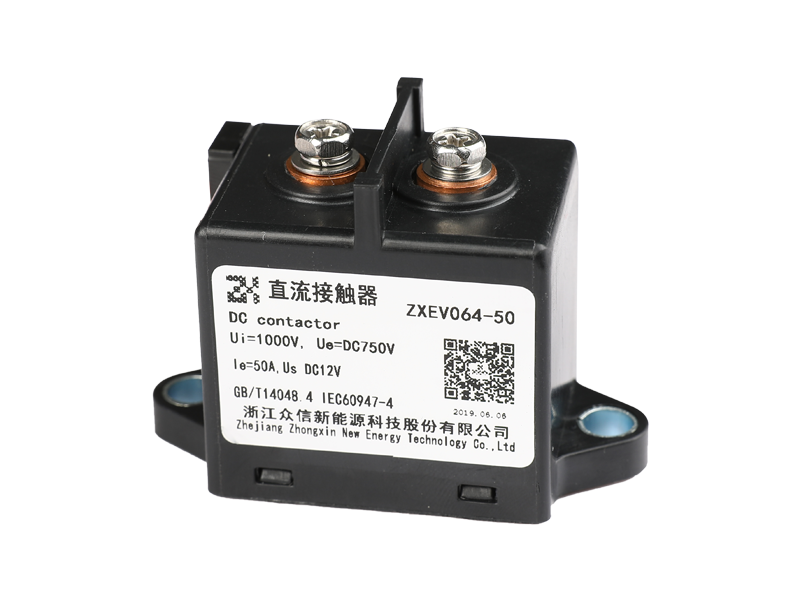
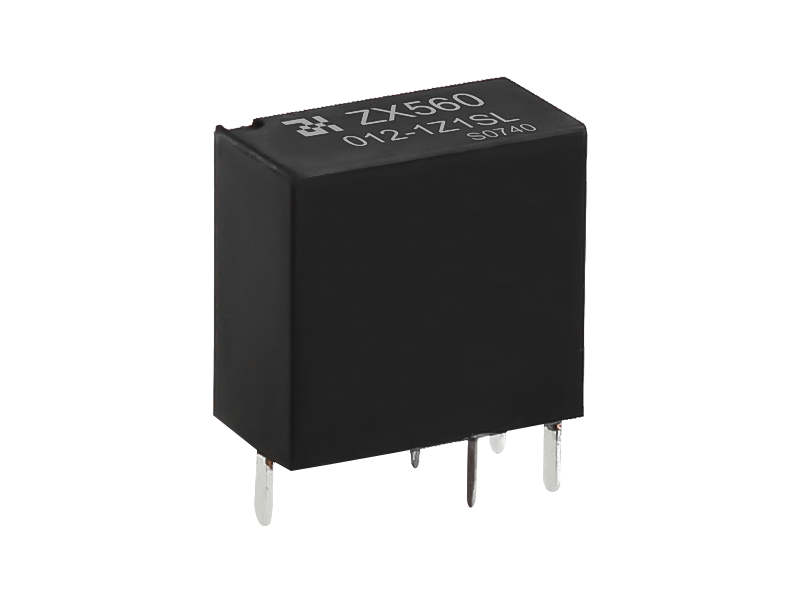
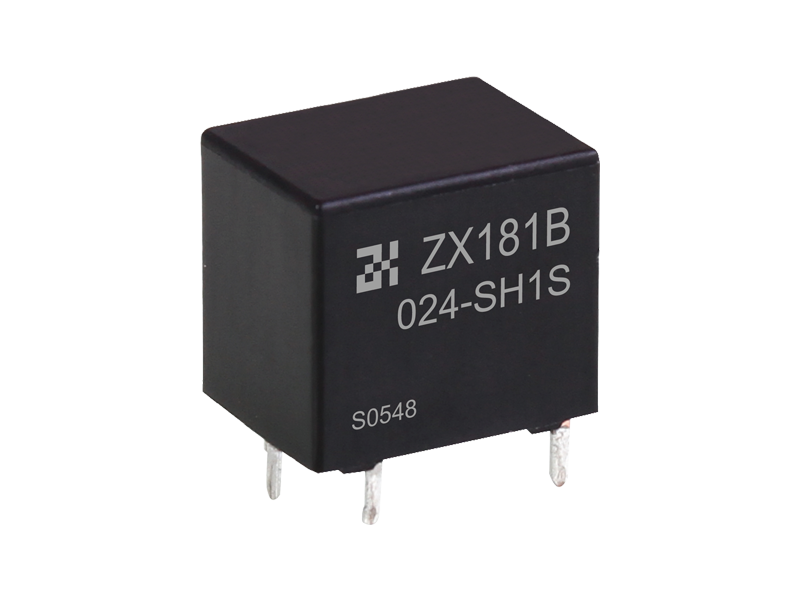
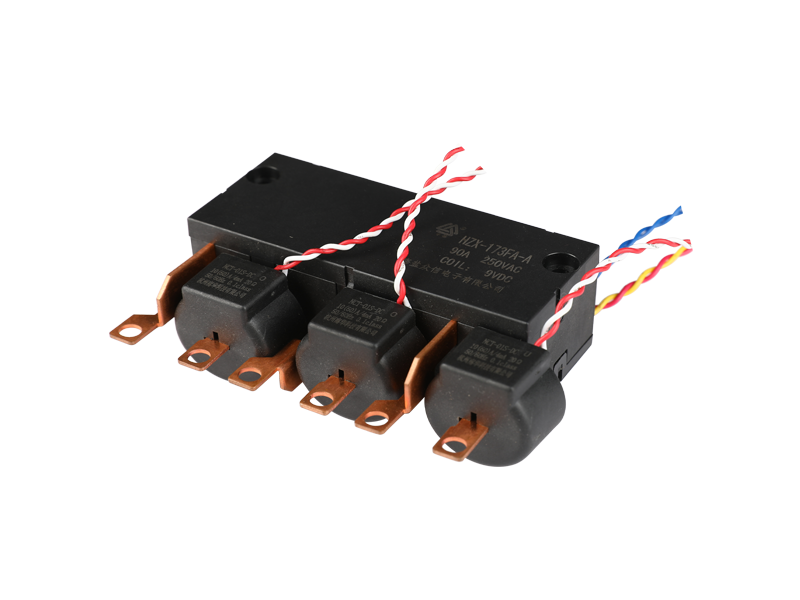
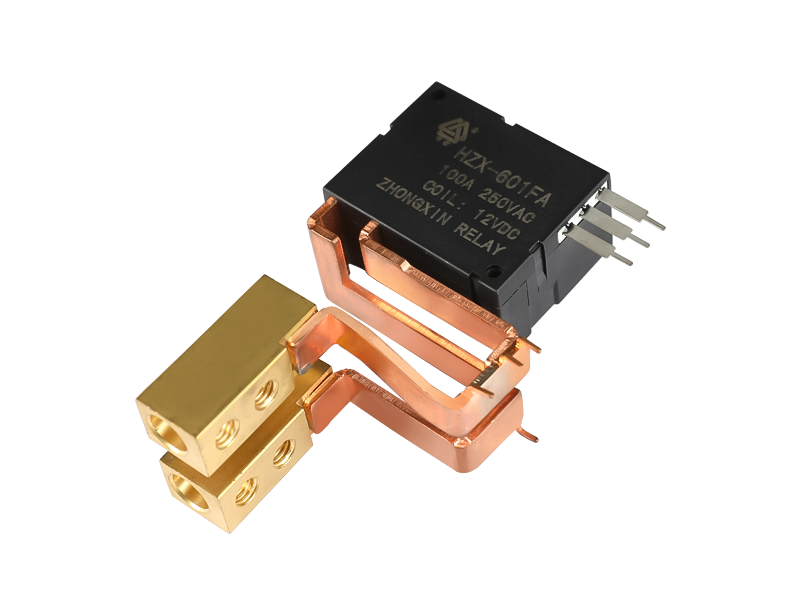
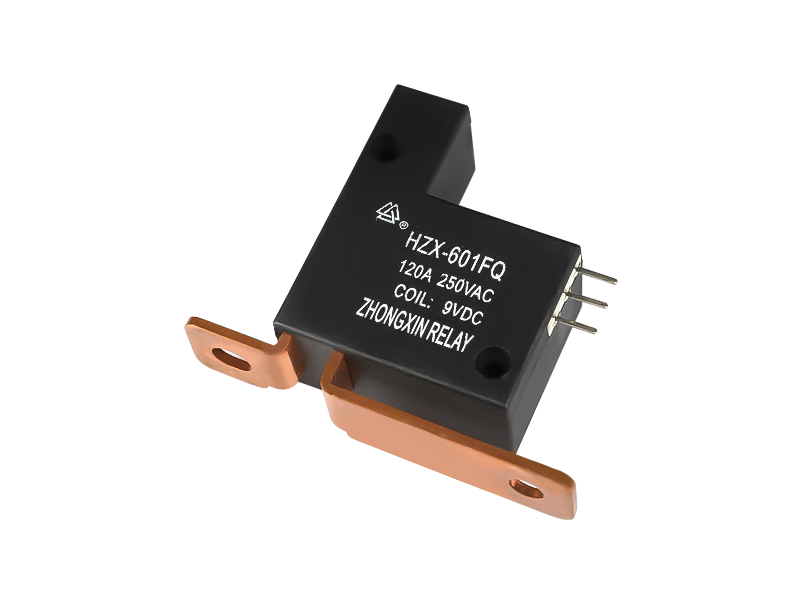
An epoxy medium-pressure DC contactor, also known as an epoxy-sealed medium-voltage DC contactor, is an electrical switching device used to control the flow of direct current (DC) in medium-voltage applications. It is designed to handle higher currents and voltages compared to low-voltage contactors commonly used in low-power applications.
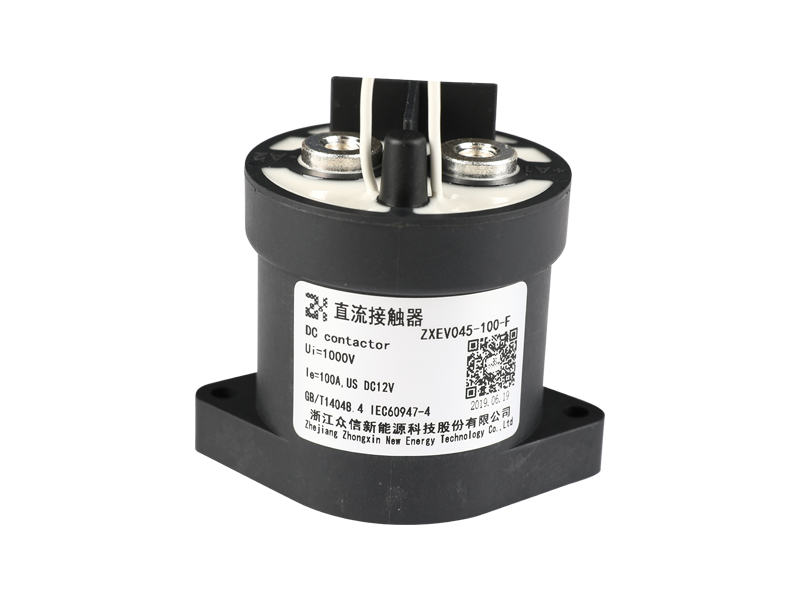

Here's a general overview of how an epoxy medium-pressure DC contactor works:
Construction: The contactor typically consists of a coil, main contacts, an arcing chamber, and an epoxy resin enclosure. The entire assembly is enclosed in epoxy to provide insulation, protection against environmental factors, and to prevent the release of harmful gases in case of arc events.
Coil and Magnetic System: When an electrical current is applied to the coil, it generates a magnetic field. The coil is typically made of copper wire or other conductive material. The magnetic field produced by the coil creates a force that acts on the moving parts of the contactor.
Main Contacts: The main contacts are the primary conducting elements of the contactor. When the coil is energized, the magnetic force attracts the moving part of the contactor towards the fixed contacts, closing the circuit and allowing the flow of current.
Arcing Chamber: During the switching process, an arc may be formed between the opening contacts. The arcing chamber is designed to facilitate the quenching of this arc. The arc is rapidly cooled and extinguished to prevent damage to the contacts and to ensure a clean and reliable breaking of the current flow.
Epoxy Enclosure: The entire contactor assembly is encapsulated in epoxy resin, which provides several advantages. It offers electrical insulation to prevent current leakage and ensures the contactor can withstand high operating voltages. The epoxy also protects the internal components from moisture, dust, and other environmental factors, making the contactor suitable for various industrial and outdoor applications.
Operating Mechanism: The contactor can be operated manually or through electronic control systems. In industrial applications, it is usually integrated into control panels or automation systems to enable remote operation.
Safety Features:
Epoxy medium-pressure DC contactors often come with additional safety features, such as auxiliary contacts for status monitoring, thermal protection to prevent overheating, and arc fault detection mechanisms for enhanced safety and reliability.
These contactors are commonly used in applications like electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, battery storage systems, and other medium-voltage DC power distribution systems. Their robust design and epoxy encapsulation make them reliable and suitable for demanding environments.