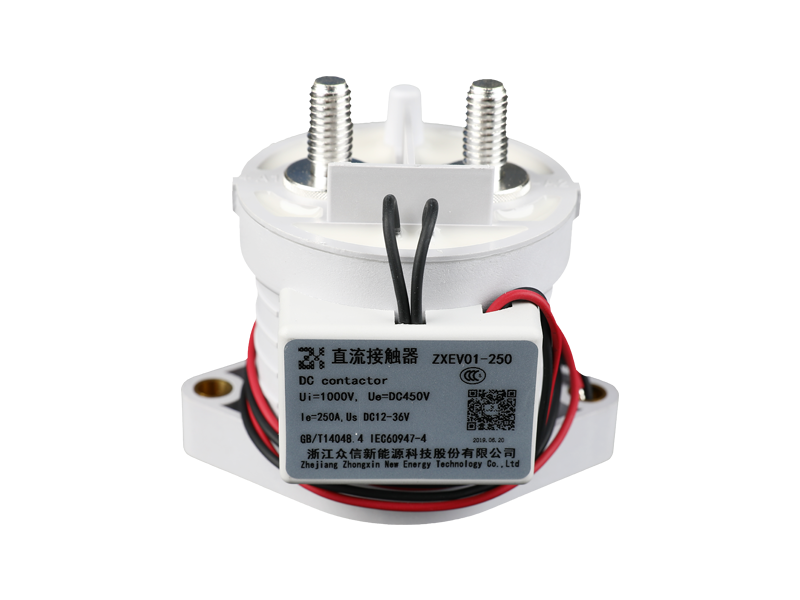
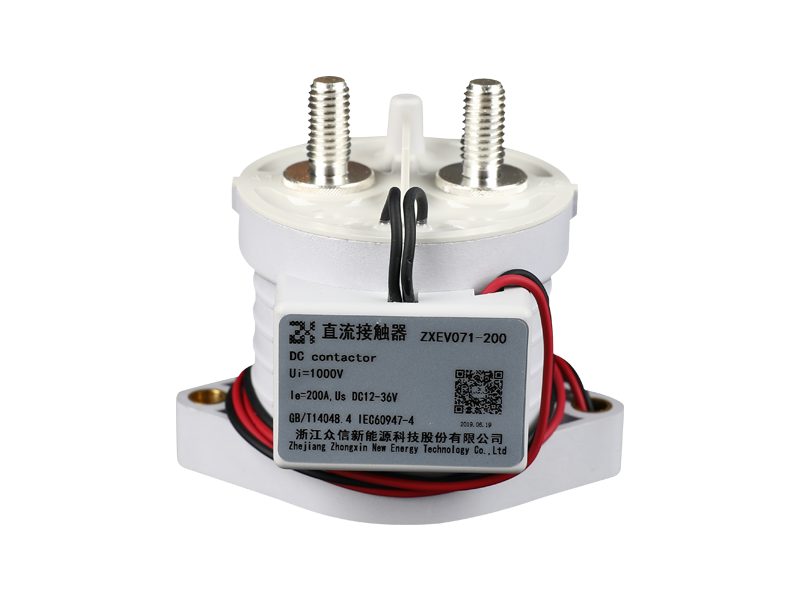
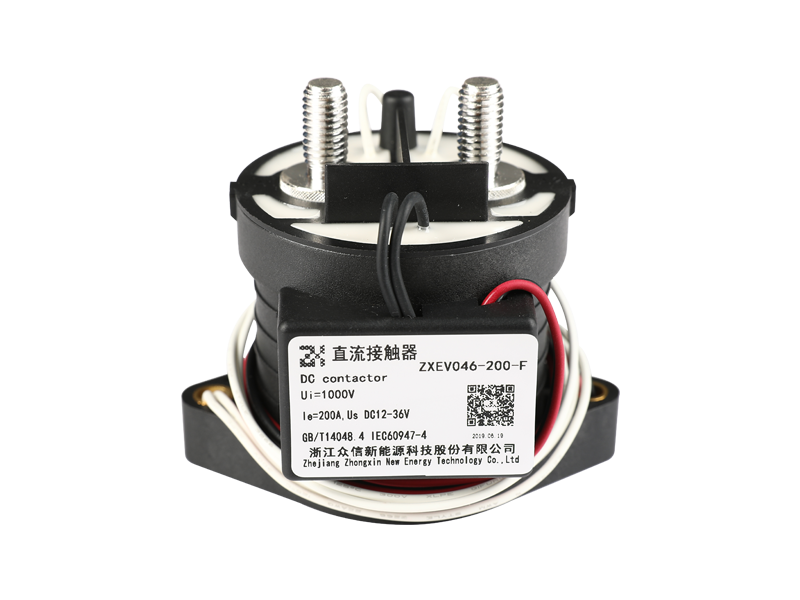
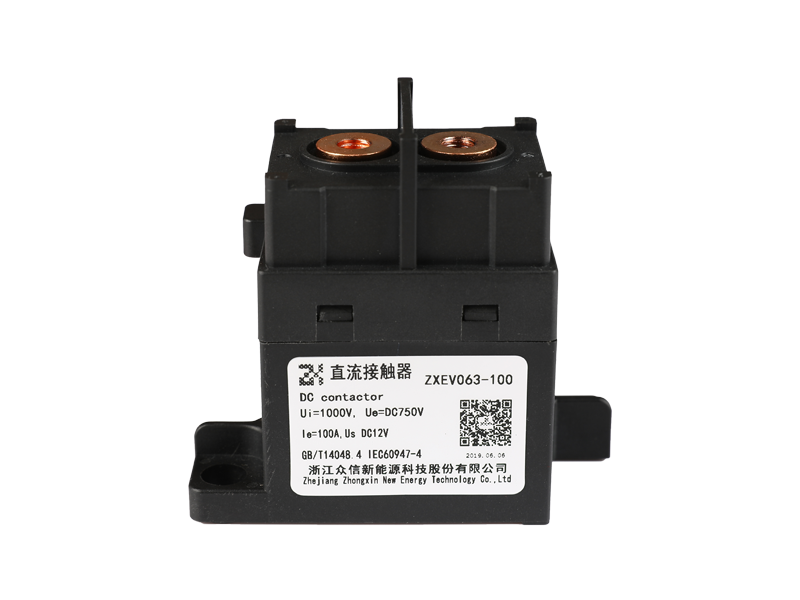
In the rapidly evolving field of electrical power conversion, safety, reliability, and efficiency remain at the core of innovation. Among various switching and protection devices, the ceramic high voltage direct current relay has emerged as a critical component in modern electrical systems. Its unique ceramic insulation structure offers exceptional dielectric strength, sealing performance, and thermal stability—characteristics that are redefining the standards for high voltage DC applications across electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial automation.
Ceramic insulation lies at the heart of high voltage DC relay performance. Unlike polymer or epoxy-based insulation, ceramic materials provide significantly higher dielectric strength and resistance to thermal degradation. These properties ensure safe switching of high current loads under operating conditions without risk of surface tracking or dielectric breakdown.
When handling voltages exceeding 1000V and currents beyond 200A, insulation integrity becomes non-negotiable. The ceramic body of a high voltage DC relay offers arc isolation during contact operation, preventing carbonization or gas expansion that could otherwise compromise the contact gap. This makes ceramic high voltage DC relays ideal for applications such as battery energy storage systems, EV power circuits, and photovoltaic converters, where long-term insulation reliability directly impacts system safety.
The construction of a ceramic high voltage DC relay integrates multiple advanced materials, each serving a distinct functional purpose. The ceramic enclosure forms a hermetically sealed environment, isolating the internal contacts and magnetic actuator from external humidity, dust, or corrosive gases.
| Component | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Housing | High-purity alumina ceramic | Provides dielectric insulation and mechanical rigidity |
| Contacts | Silver or tungsten alloy | Ensures low resistance and arc erosion resistance |
| Actuator | Electromagnetic coil | Enables fast switching response |
| Sealing medium | Inert gas or vacuum | Prevents oxidation and extends relay life |
This structural configuration allows the ceramic sealed DC relay to operate in environments with high temperature gradients or vibration, maintaining stable insulation resistance even after thousands of switching cycles. The hermetic sealing also eliminates the risk of moisture ingress—a critical factor in long-term field reliability.
One of the defining performance features of a high voltage DC contact relay is its arc suppression capability. During switching, the rapid separation of contacts can generate high-energy arcs that degrade materials and shorten device lifespan. The ceramic housing of the HVDC relay supports efficient heat dissipation while working in tandem with internal arc extinguishing mechanisms, such as magnetic blowout structures or gas-filled chambers.
Ceramic’s inherent high thermal conductivity ensures that localized hot spots do not accumulate, reducing contact wear and preserving electrical performance over time. Furthermore, its non-conductive and non-flammable nature enhances system safety, even in compact or high-density installations such as EV battery packs or solar inverter systems.
Compared to plastic or epoxy-sealed DC relays, ceramic high voltage DC relays offer several crucial advantages that align with the increasing demands for compactness, safety, and long operating lifetimes.
| Feature | Ceramic HVDC Relay | Polymer/Resin Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | Very high (10–20 kV/mm) | Moderate (3–5 kV/mm) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, up to 250°C | Limited, up to 120°C |
| Sealing Performance | Hermetic, moisture-proof | Partial, subject to leakage |
| Arc Resistance | Superior | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Extended under high load | Reduced under heat stress |
This comparison highlights why the shift toward ceramic-based high voltage switching components is accelerating, particularly in sectors where system downtime or electrical failure carries high operational risks.
The versatility of ceramic high voltage DC relays allows their deployment across a broad range of high-voltage DC platforms, where reliability and insulation strength are critical design considerations.
Key application areas include:
Electric Vehicles (EVs): Battery disconnection, motor control, and fast-charging systems rely on high current DC relays with compact size and high dielectric isolation.
Energy Storage Systems: Ceramic HVDC relays protect and isolate battery modules, ensuring stable operation under fluctuating current loads.
Renewable Energy: In photovoltaic and wind systems, high voltage DC contact relays manage energy conversion circuits and inverter protection.
Industrial Automation: Machines requiring DC power control benefit from hermetically sealed ceramic relays resistant to dust and oil exposure.
These applications demand high insulation resistance, low contact resistance, and long-term mechanical endurance—all performance areas in which ceramic technology excels.
| Specification | Typical Range | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 750–1500 V DC | Defines insulation and contact gap requirements |
| Rated Current | 50–300 A | Determines thermal load capacity |
| Contact Resistance | ≤ 0.5 mΩ | Influences efficiency and heating |
| Insulation Resistance | ≥ 10⁹ Ω | Ensures leakage-free operation |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C | Enables use in harsh conditions |
| Mechanical Life | Up to 1,000,000 cycles | Supports long-term reliability |
Such parameters reflect the delicate balance between electrical performance, thermal stability, and mechanical endurance that ceramic technology enables.
The ceramic high voltage direct current relay represents more than an incremental improvement in electrical switching—it signifies a foundational shift toward safer, more durable, and higher-performing insulation technologies. By leveraging the dielectric properties of ceramics, engineers can achieve compact designs capable of sustaining demanding voltage and temperature conditions without compromising reliability.