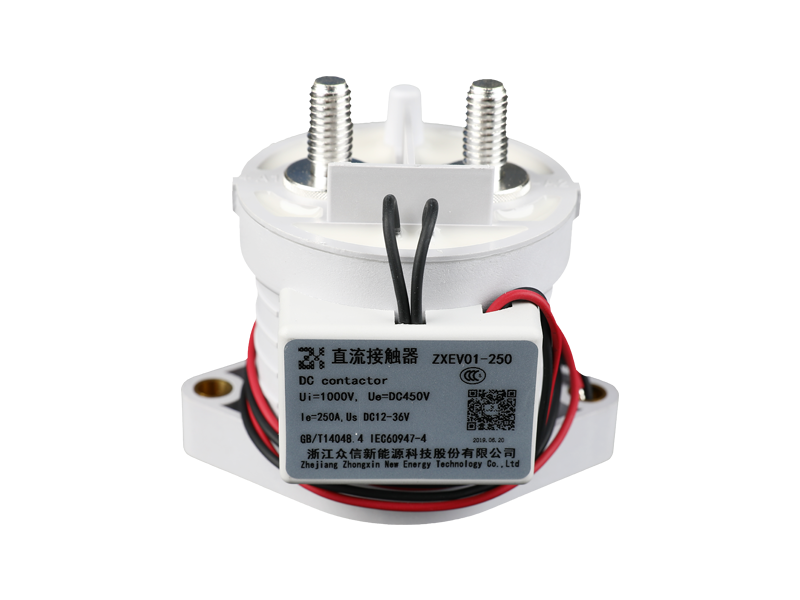
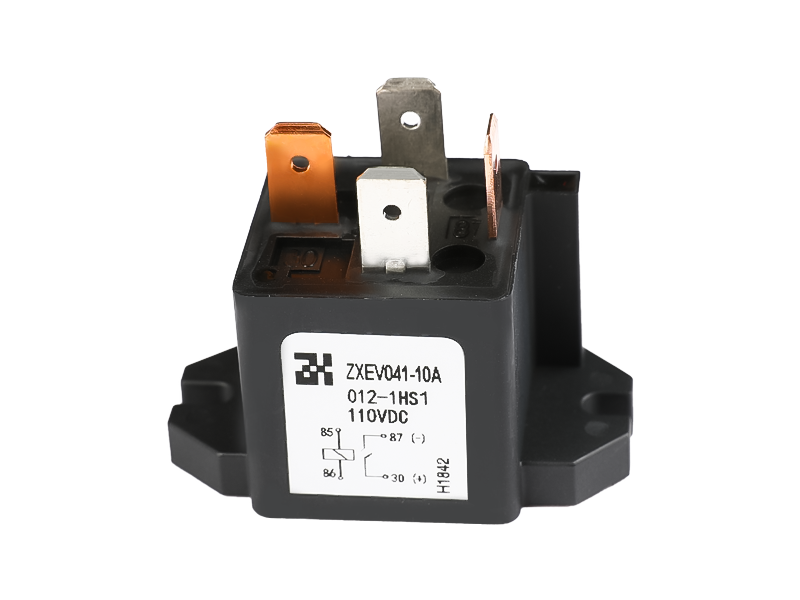
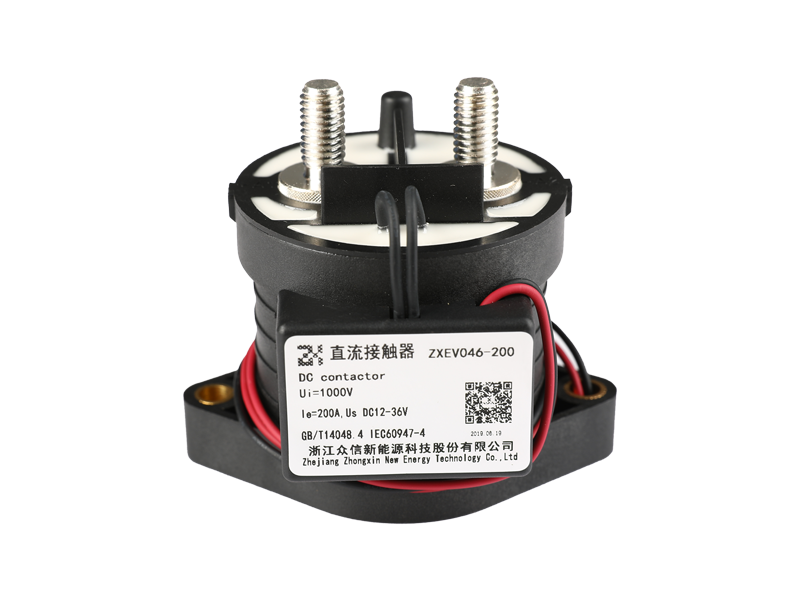
The demand for reliable and efficient high voltage power systems has surged, driven by the growth of electric vehicles, renewable energy integration, and advanced industrial automation. At the heart of these systems lies a critical component: high voltage direct current contactors. These devices play a pivotal role in controlling and protecting DC power circuits, ensuring both operational safety and system longevity.
High voltage direct current contactors are electromechanical devices designed to make or break DC electrical circuits under load conditions. Unlike AC systems, DC circuits do not have zero-crossing points, which means interrupting current flow generates higher arc energy. This makes the design and operation of high voltage direct current contactors inherently more challenging.
The core functions of these devices include:
Key advantages of modern high voltage direct current contactors include compact design, fast switching capability, and high reliability under frequent operation conditions.
High voltage direct current contactors are widely used in:
The operation of high voltage direct current contactors is based on the interaction of electromagnetic and mechanical systems. Their fundamental principle can be broken down into several stages:
When a control voltage is applied to the coil of a contactor, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field exerts a force on the movable armature, causing it to move toward the stationary contacts. This movement closes the circuit, allowing current to flow.
Conversely, when the control voltage is removed, a spring mechanism retracts the armature, opening the contacts and interrupting current flow. The absence of zero-crossing in DC circuits means that the contacts must withstand sustained arcing energy, which is typically managed by arc extinguishing mechanisms.
Since DC current does not naturally pass through zero, arcs tend to be more persistent compared to AC systems. Modern high voltage direct current contactors employ several methods to manage arcs:
| Arc Management Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic blowout | Uses a magnetic field to elongate and move the arc away from contacts | Reduces contact wear |
| Arc chute | Directs the arc into a series of insulating plates to cool and extinguish it | Enhances interruption capability |
| Contact material selection | High-melting point alloys like silver-tungsten | Increases durability and reliability |
These mechanisms ensure that the contactor can operate safely under high-voltage DC conditions, even in frequent switching scenarios.
The contacts of high voltage direct current contactors are specifically engineered to endure high-energy arcing and mechanical stress. Common design considerations include:
Proper contact design significantly extends the operational lifespan of the device and minimizes maintenance needs.
Modern high voltage direct current contactors often integrate control electronics for enhanced functionality. These may include:
Integrating such sensors not only improves safety but also allows predictive maintenance, reducing system downtime.
When selecting high voltage direct current contactors, several technical parameters must be considered:
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Rated voltage | Maximum DC voltage the contactor can handle | 600V – 1500V |
| Rated current | Maximum continuous current | 50A – 1000A |
| Mechanical life | Number of operational cycles without load | 1,000,000+ cycles |
| Electrical life | Number of operational cycles under full load | 100,000 – 500,000 cycles |
| Operating temperature | Safe working temperature range | -40°C to 85°C |
These parameters ensure proper device selection for specific applications and environmental conditions.
Designing a reliable high voltage direct current contactor involves multiple engineering aspects:
By carefully balancing these factors, manufacturers can produce contactors that meet both safety and performance requirements.
High voltage direct current contactors must comply with industry safety standards, including electrical isolation, dielectric strength, and short-circuit withstand ratings. Proper adherence ensures protection against:
Standards also guide testing procedures to validate operational reliability under conditions.
Q1: What is the main difference between DC and AC contactors?
DC contactors must handle continuous current without zero-crossing, which causes persistent arcs. AC contactors benefit from natural current zero-crossing, making arc extinction easier.
Q2: Why are high voltage direct current contactors critical for electric vehicles?
They safely switch high-voltage battery packs, protect downstream electronics, and enable maintenance isolation.
Q3: How is arc suppression achieved in DC contactors?
Through techniques like magnetic blowout, arc chutes, and high-resistance contact materials that dissipate and extinguish the arc.
Q4: What are key selection parameters for these devices?
Rated voltage and current, mechanical and electrical life, operating temperature, and arc extinguishing capability.
Q5: Can DC contactors be integrated with smart monitoring systems?
Yes, modern devices often include sensors for position, temperature, and current, enabling predictive maintenance and remote monitoring.