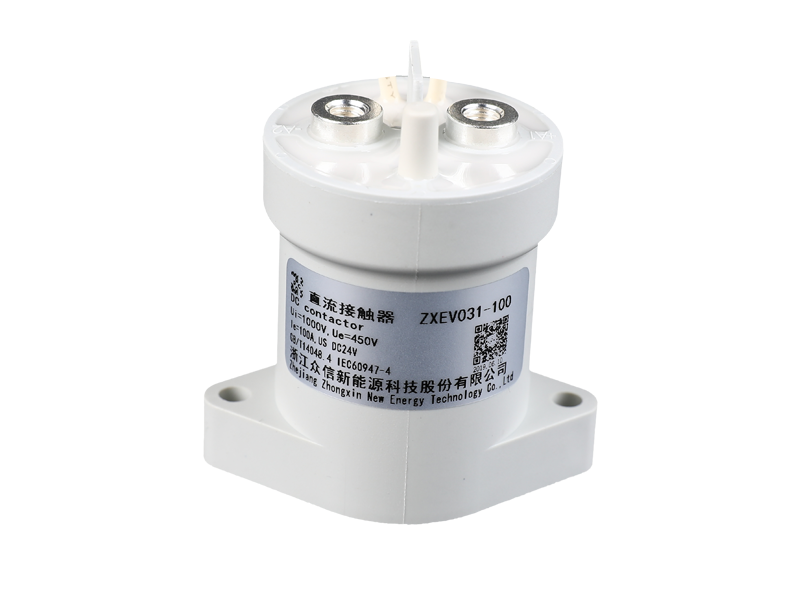
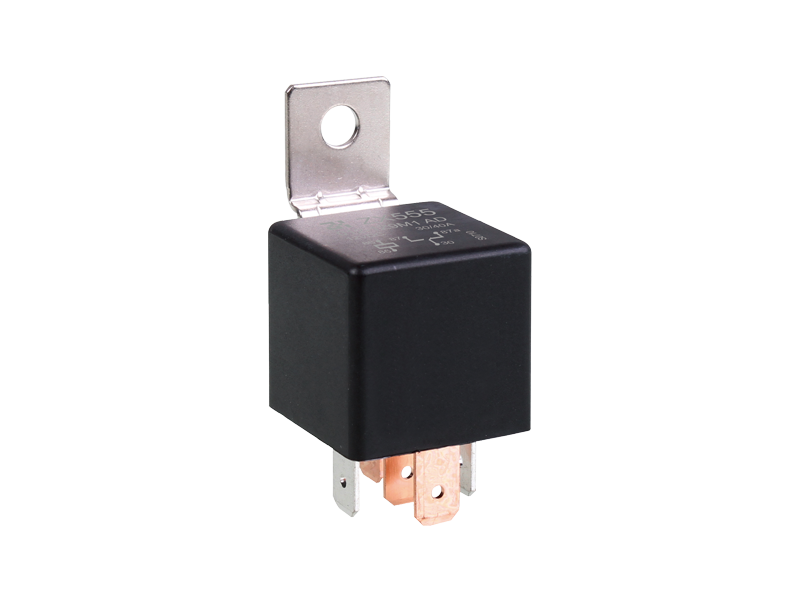
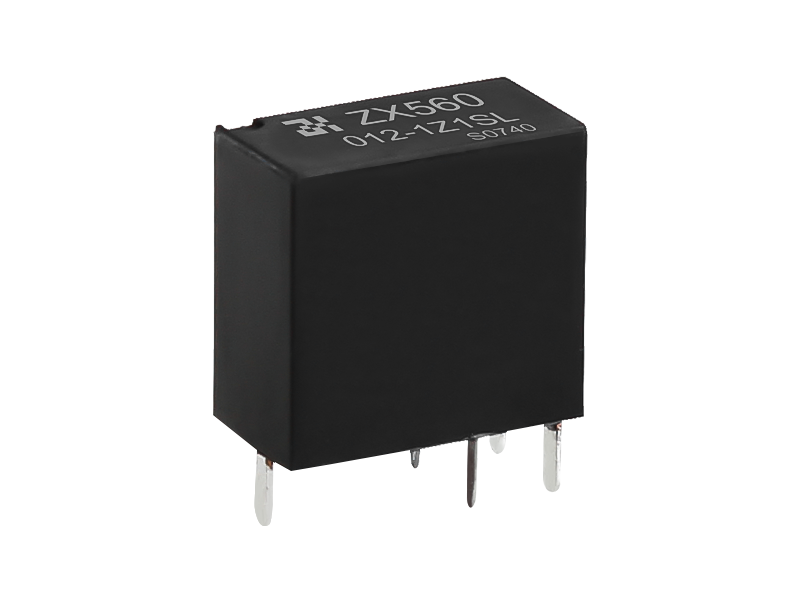
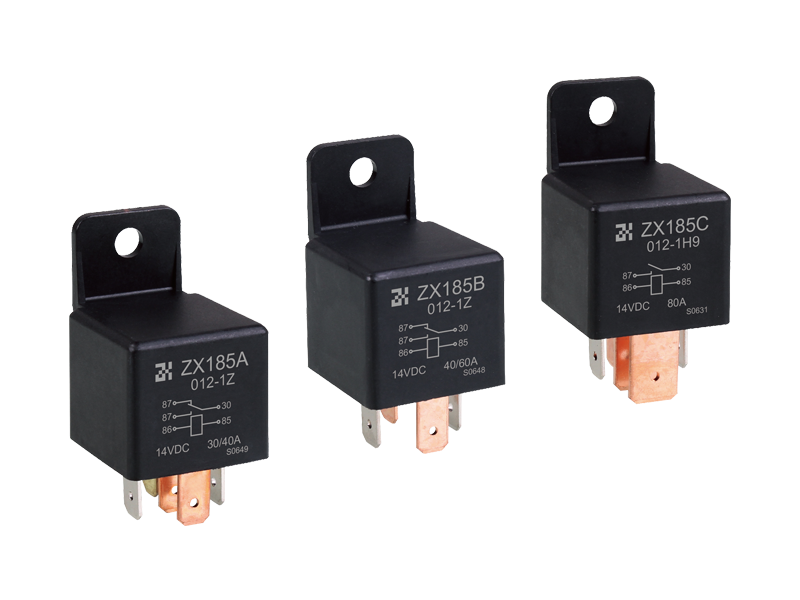
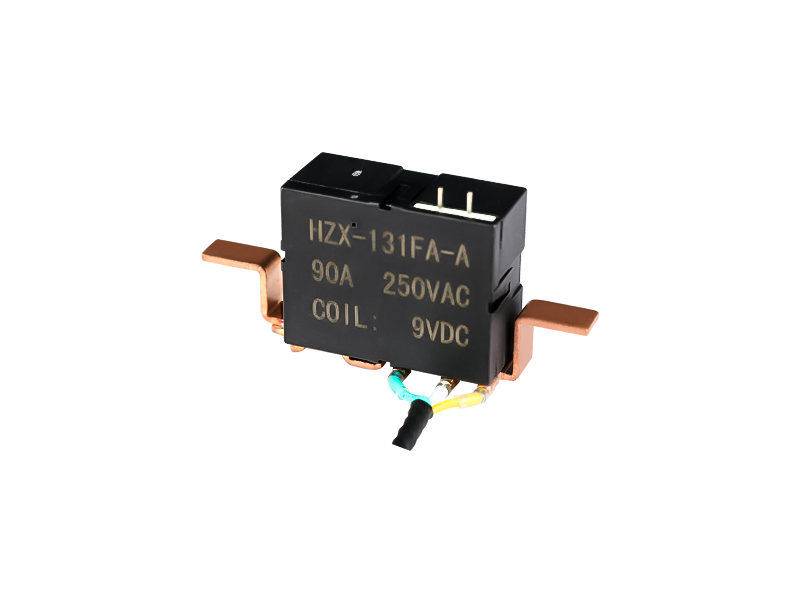
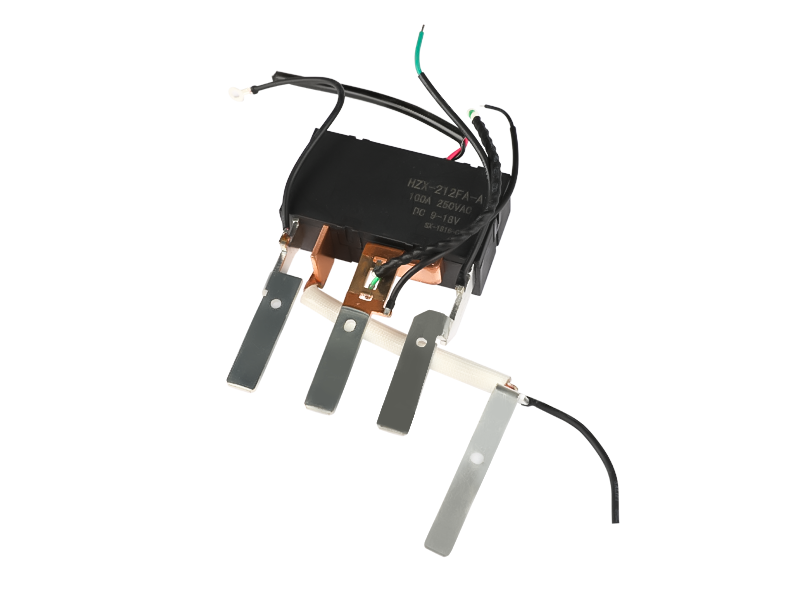
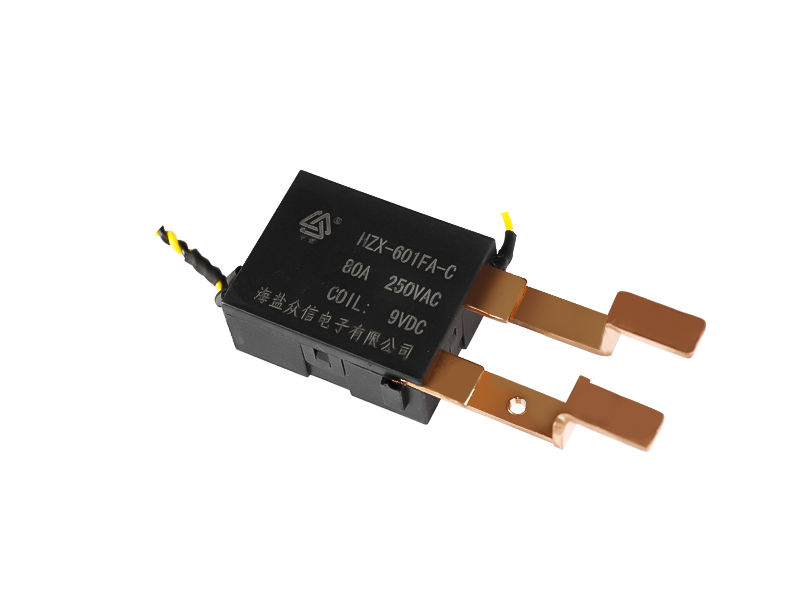
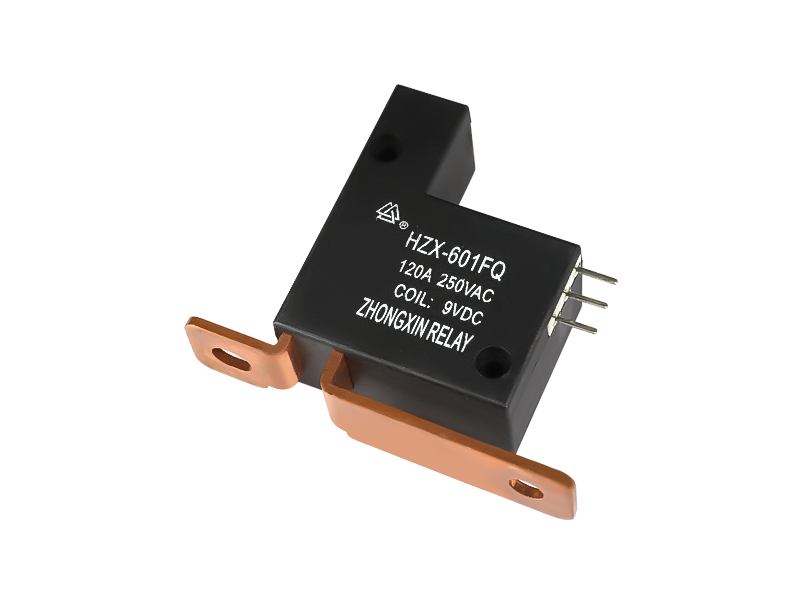
Electromagnetic relays are generally composed of iron cores, coils, armatures, contact reeds, etc. As long as a certain voltage is applied to both ends of the coil of the relay module, a certain current will flow through the coil, which will produce electromagnetic effects. Under the action of the electromagnetic force, the armature will overcome the pulling force of the return spring and attract to the iron core. The moving contact and the static contact (normally open contact) that drive the armature are pulled together. When the coil is de-energized, the electromagnetic attraction will disappear, and the armature will return to its original position under the reaction force of the spring, releasing the moving contact and the original static contact (normally closed contact). This pulls in and releases, so as to achieve the purpose of conducting and cutting off in the circuit. The "normally open and normally closed" contacts of the relay can be distinguished as follows: the static contact that is in the off state when the relay coil is not energized is called "normally open contact"; the static contact that is in the on-state is called It is a "normally closed contact". Relays generally have two circuits, a low-voltage control circuit, and a high-voltage working circuit.
The relay has the following functions:
Expand the scope of control:For example, when the control signal of a multi-contact relay module reaches a certain value, different forms of the point group of the touch relay module can be touched, and multiple circuits can be switched, disconnected, and connected at the same time.
enlarge:For example, sensitive relays, intermediate relays, etc., with a very small control quantity, can control a circuit with large power.
Comprehensive signal:For example, when a plurality of control signals are input to a multi-winding relay in a prescribed form, they will be compared and integrated to achieve a predetermined control effect.
Automatic, remote control, monitoring:For example, the relay on the automatic device and other electrical appliances can form a program control circuit to realize automatic operation.