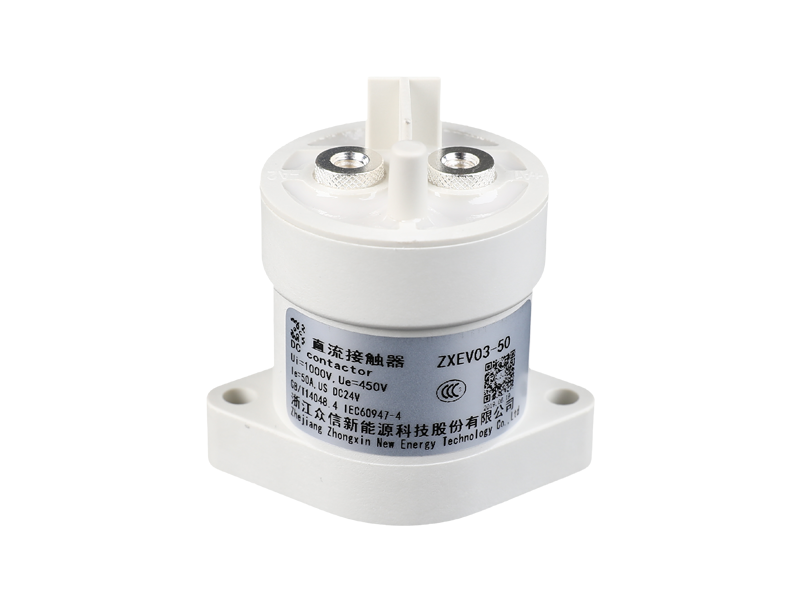
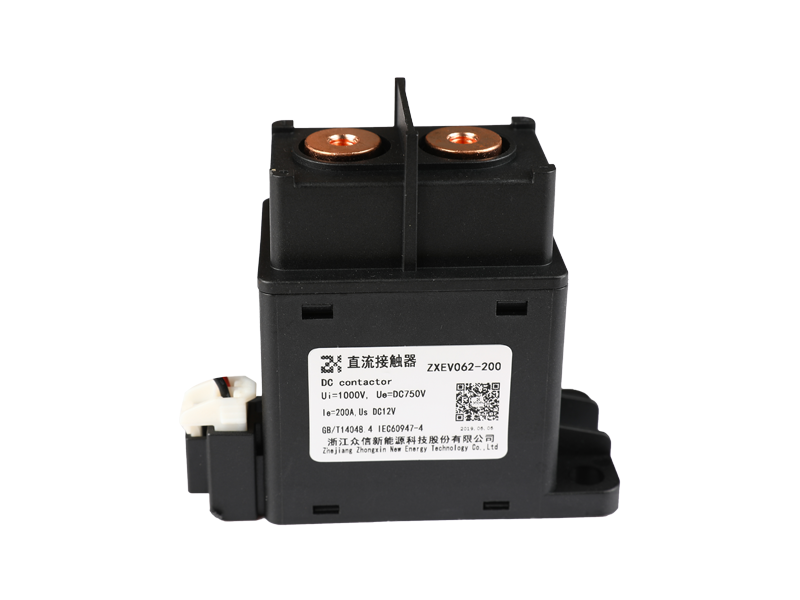
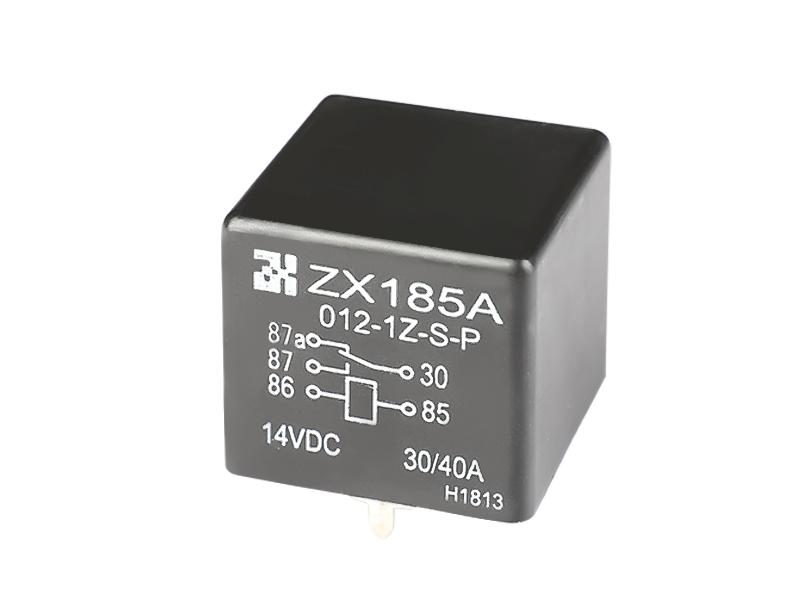
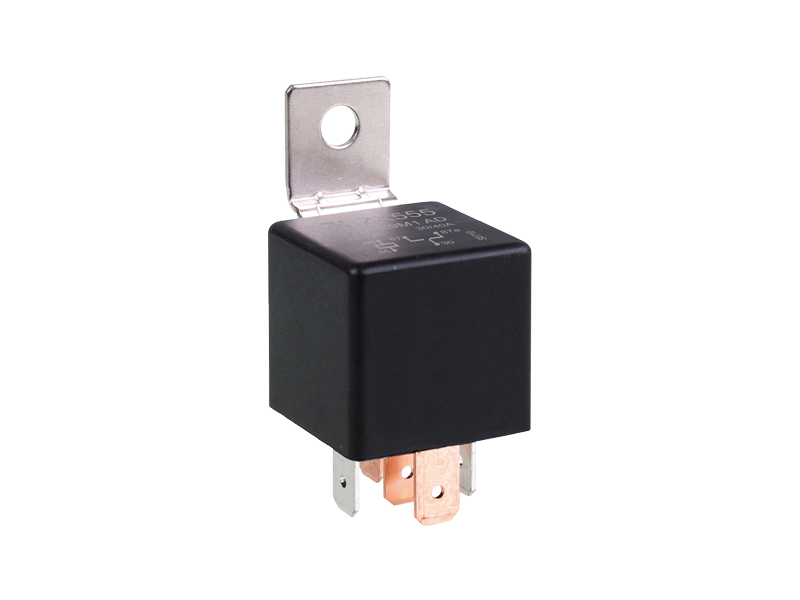
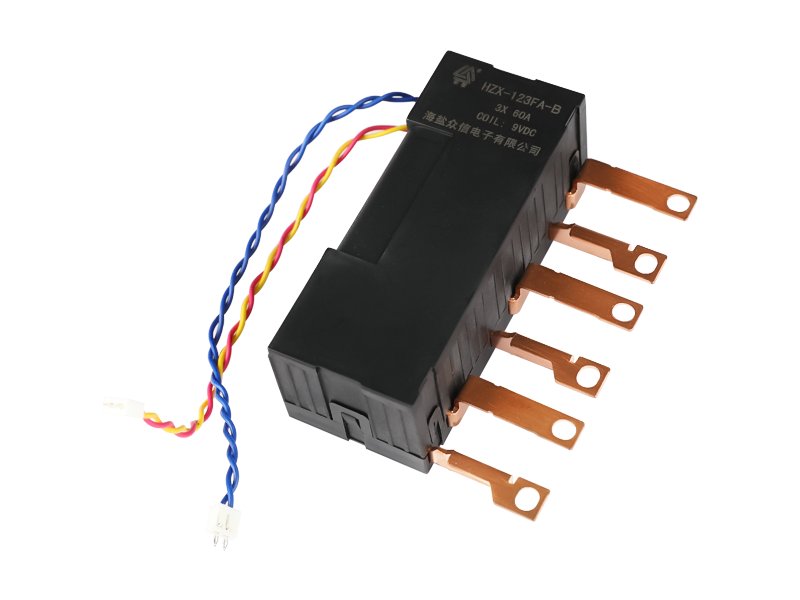
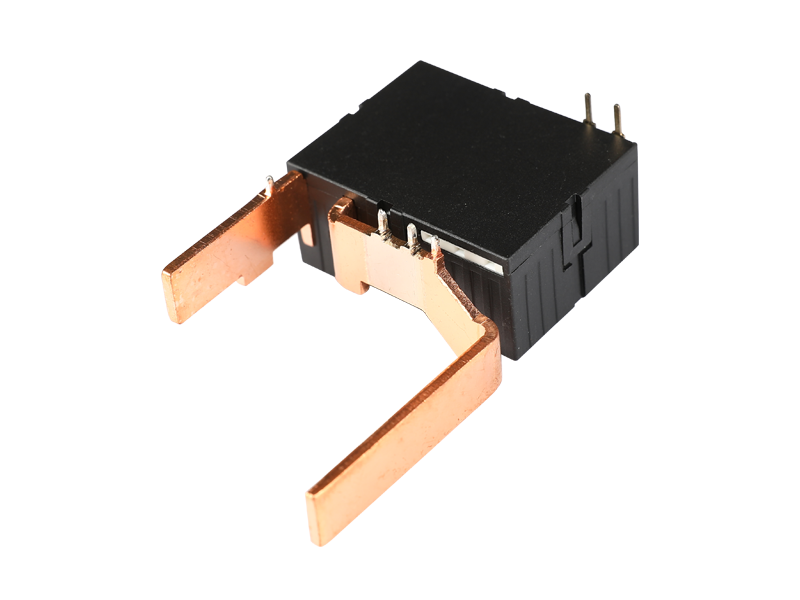
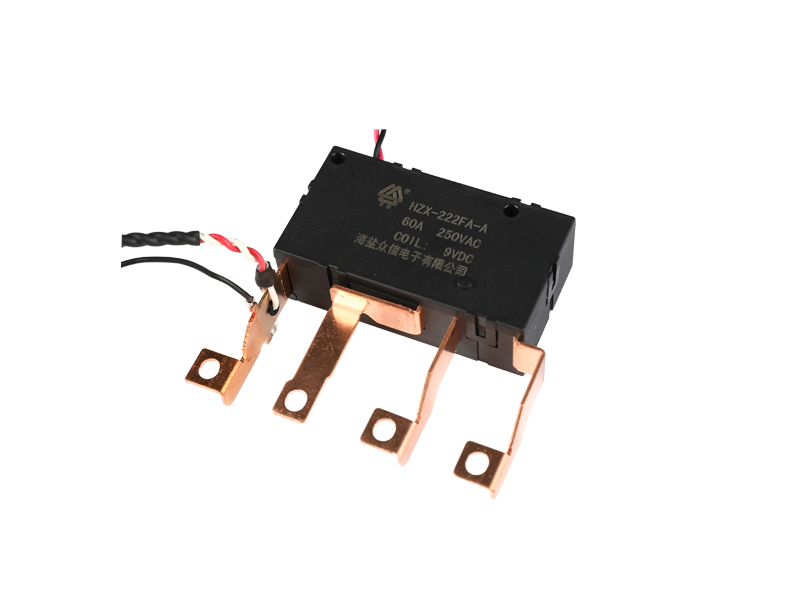
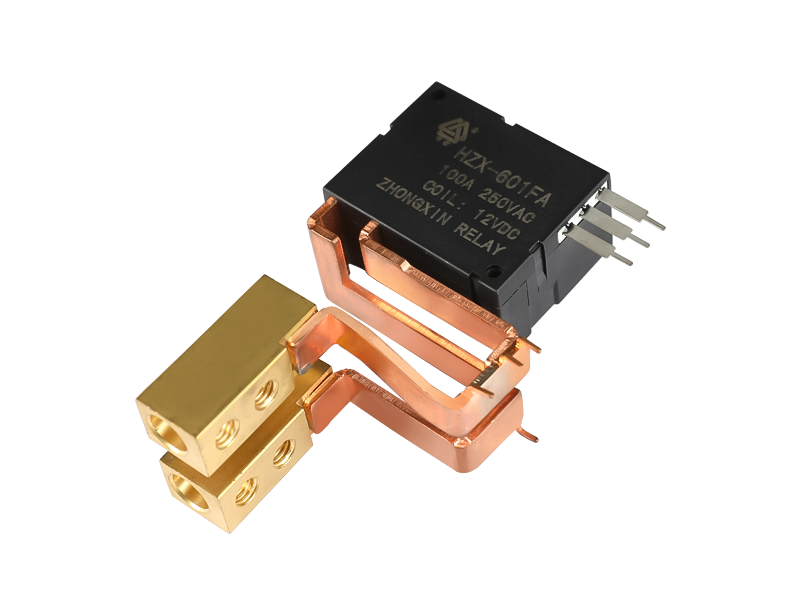
The main classification and functions of voltage relays:
1) Electromagnetic relay: use the circuit in the input circuit to connect the core of the electromagnet
2) Solid-state relay: refers to a kind of relay in which electronic components perform their functions without mechanical moving components, and the input and output are isolated.
3) Temperature relay: a relay that acts when the outside temperature reaches a given value.
4) Reed relay: a relay that is sealed in the tube and has the double action of the electric shock reed and the armature magnetic circuit to open, close or switch the circuit
5) Time relay: When the input signal is added or removed, the output part needs to be delayed or limited to the specified time before closing or disconnecting its controlled circuit relay.
6) High frequency relays with the minimum loss for switching high frequency, radio frequency lines.
7) Polarized relay: a relay that has the combined action of the polarized magnetic field and the magnetic field generated by the control current through the control coil. The direction of action of the relay depends on the direction of the current flowing in the control coil.
8) Other types of relays: such as photo relays, acoustic relays, thermal relays, instrumentation relays, Hall effect relays, differential relays, etc.
The main function of the voltage relay:
Relay is an automatic switching element with an isolation function. It is widely used in remote control, telemetry, communication, automatic control, mechatronics, and powers electronic equipment. It is one of the most important control elements.
The relay generally has an induction mechanism (input part) that can reflect certain input variables (such as current, voltage, power, impedance, frequency, temperature, pressure, speed, light, etc.); Between the input port and the output port of the relay, there is an intermediate mechanism (drive part) that couples and isolates the input quantity, processes the function and drives the output part.
As a control element, to sum up, the relay has the following functions:
1) Expand the control range: For example, when the control signal of the multi-contact relay reaches a certain value, it can switch, break, and connect multiple circuits at the same time according to different forms of the contact group.
2) Amplification: For example, sensitive relays, intermediate relays, etc., with a very small amount of control, can control circuits with high power.
3) Integrated signal: For example, when multiple control signals are input to the multi-winding relay in a prescribed form, the predetermined control effect can be achieved through comparison and synthesis.
4) Automatic, remote control, and monitoring: For example, the relay on the automatic device can form a program control circuit together with other electrical appliances to realize automatic operation.