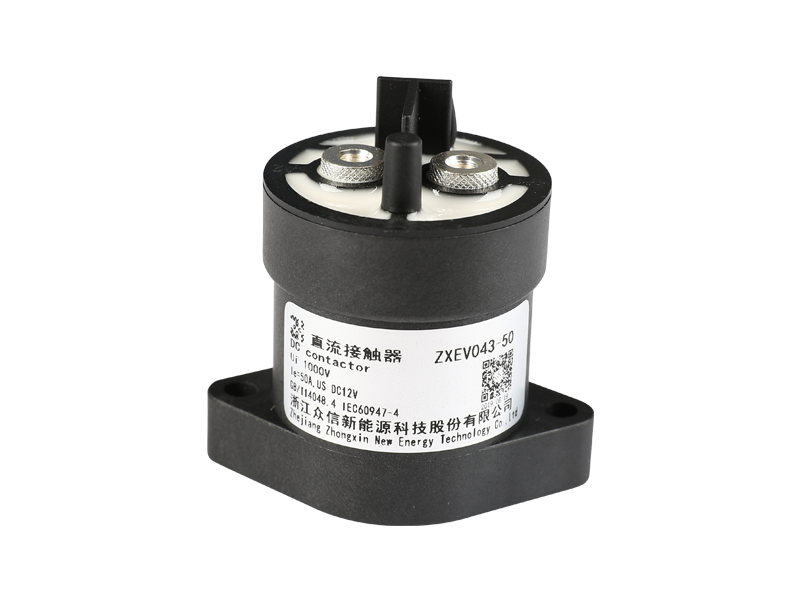
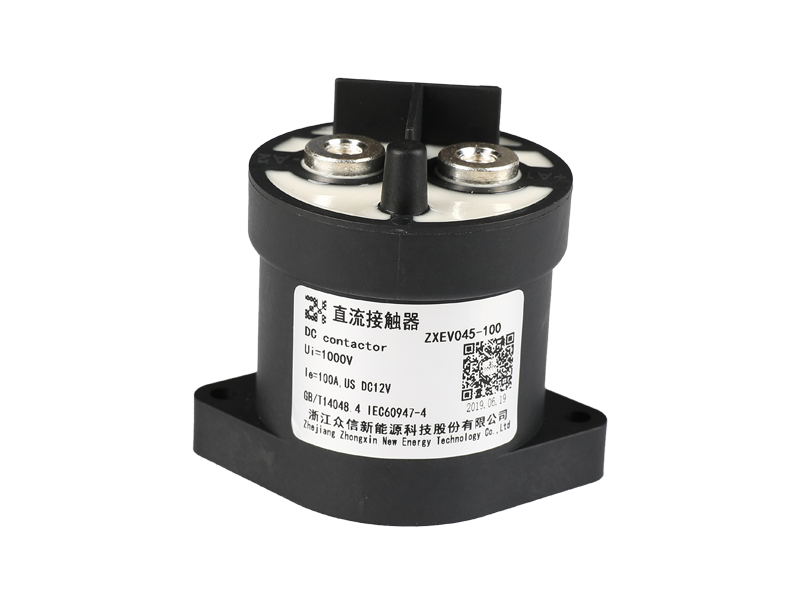
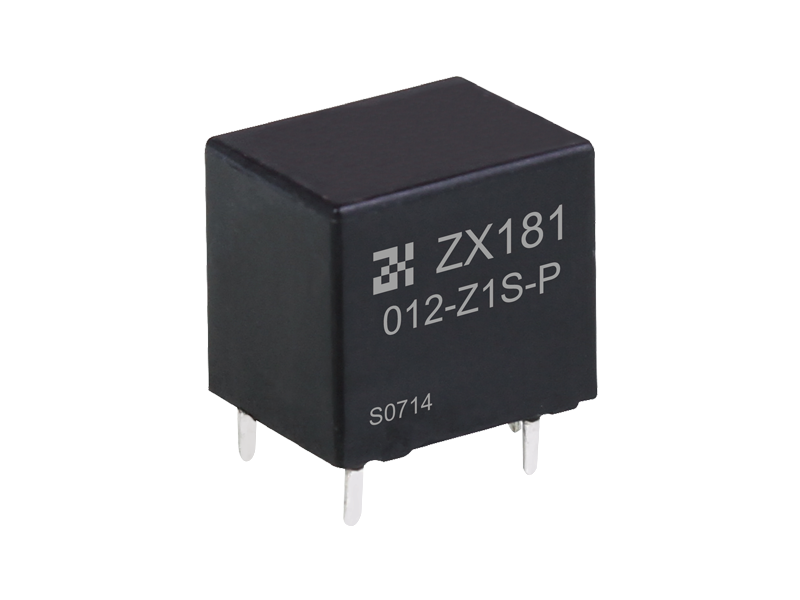
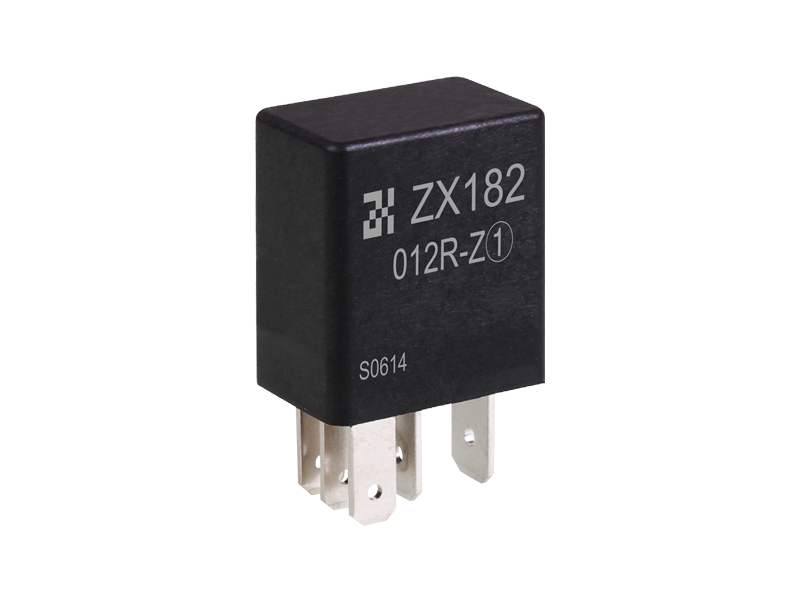
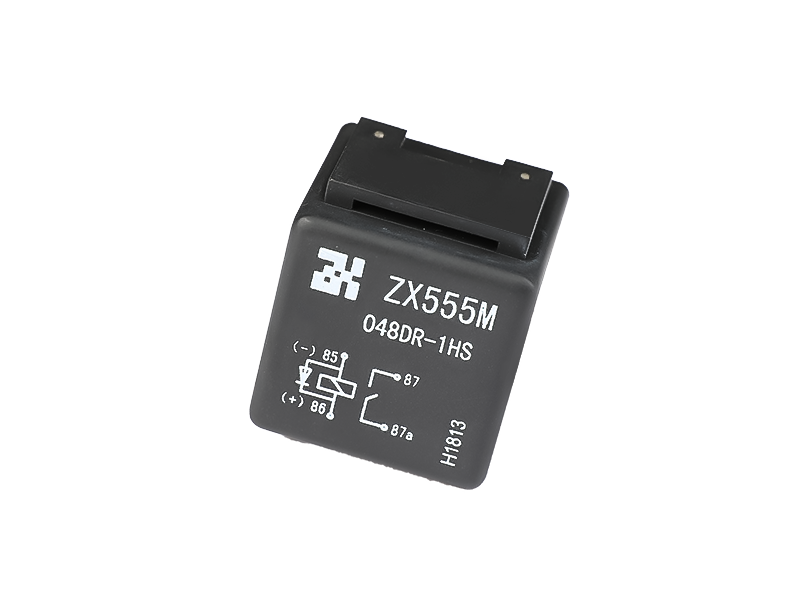
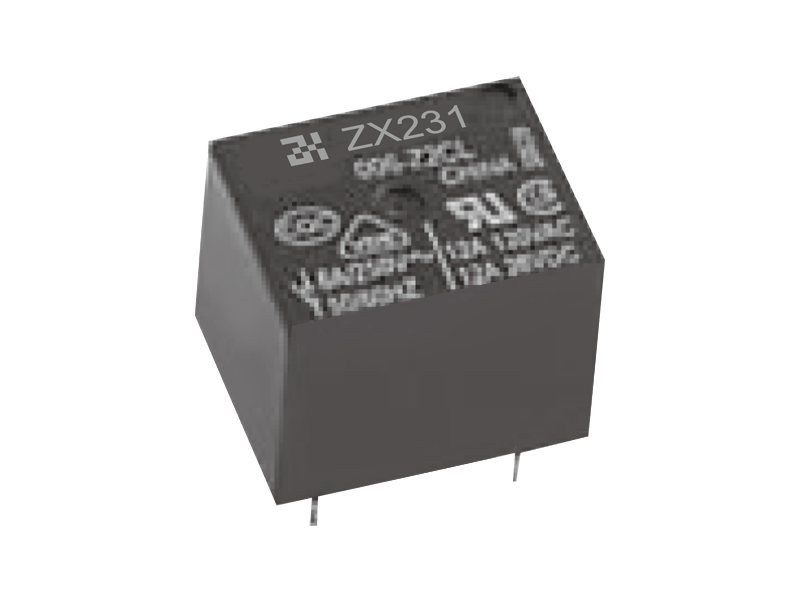
Relay (English name: relay) is an electrical control device, which is an electrical appliance that causes the controlled quantity to undergo a predetermined step change in the electrical output circuit when the change of the input quantity (excitation quantity) meets the specified requirements. It has an interactive relationship between the control system (also known as the input loop) and the controlled system (also known as the output loop). Usually used in automatic control circuits, it is actually an "automatic switch" that uses a small current to control the operation of a large current. Therefore, it plays the role of automatic adjustment, safety protection, and conversion circuit in the circuit.
Relay is an automatic switching element with isolation function, widely used in remote control, telemetry,
It is one of the most important control components in communication, automatic control, mechatronics and power electronic equipment.
Relays generally have induction mechanisms (input parts) that can reflect certain input variables (such as current, voltage, power, impedance, frequency, temperature, pressure, speed, light, etc.); "Off" control actuator (output part); between the input part and the output part of the relay, there is an intermediate mechanism (drive part) for coupling and isolation of the input, function processing and driving the output part. -WuhanHVHipot
GDJB-relayprotectiontestset/secondarycurrentinjectiontestset
Intermediate relay model, intermediate relay function and working principle
The intermediate relay is a product used in relay protection and automatic control systems to increase the number and capacity of contacts, and it is used to transmit intermediate signals in the control circuit. The following editor will take you to understand the model and working principle of the intermediate relay!
1. What is an intermediate relay
According to the role of relays in the protection circuit, relays can be divided into starting relays, measuring relays, time relays, signal relays, export relays and intermediate relays.
The structure and principle of the intermediate relay are basically the same as those of the AC contactor. The main difference from the contactor is that the main contacts of the contactor can pass a large current, while the contacts of the intermediate relay can only pass a small current. Therefore, it can only be used in control circuits. It generally does not have a main contact, because the overload capacity is relatively small. So all it uses are auxiliary contacts, and the number is relatively large. The definition of the intermediate relay in the new national standard is K, and the old national standard is KA. Usually DC power supply. A few use AC power supply.
Second, the intermediate relay model
Model Name Model List and Meaning
RZ rail type intermediate relay
Function: electromagnetic intermediate relay
Model list
DZ-10 seriesDZ-3/Z seriesDZ-(G) seriesDZ-seriesDZ-50 series
DZ-60 series DZ-series DZB-holding series DZB-(G) series holding DZB-series holding
DZBS series rail low current starter
DZB series guide rail holding relay DZJ-10 series DZK-series fast DZK-series fast
DZS-Delay series
DZS-(G) series delay DZS-delay series DZS-terminal delay series DZS-series delay
DZS series rail delay
DZY-series DZJ-series DZL-series DZY/AC series AC terminal block
DZY series DC terminal block
Function: static intermediate relay
Model list
JZ-10 seriesJZ-7(XMT)XJZY(J)(XMT) seriesJZ-7G guide rail seriesJZ-7G(XMT) series guide railJZ-7G series guide rail
JZ-7Y(J)-10, XJZY(J)--7Y(J)-, XJZY(J)--7Y(J)-30, XJZY(J)--static holding series JZB-10 static holding series
JZB-anti-jump seriesJZB-C static hold seriesJZB static hold seriesJZK-static seriesJZS-10static delay series
JZS-Static delay seriesJZS-Delay seriesJZS-7/1Delay seriesJZS-7/3Delay seriesJZS-7/、XJZS-Delay series
JZS-7/Delay seriesJZS-7/5 Delay seriesJZS-7/6Delay seriesJZS-7G(XMT)Delay seriesJZS-7G/2Delay series
JZS-7G/4 delay seriesJZS-7G/5 delay seriesJZS-7-XMT delay seriesJZS-A seriesJZS-B series
JZS-C series delay seriesJZY-delay seriesJZJ-delay seriesJZY(J)-C delay seriesJZY series
JZYJ series UEG series WZY series XJBZ-anti-jump series XJBZ-series anti-jump intermediate relay (unconventional)
ZJ2 series ZJ3-A, ZJ3-B series ZJ3-C series ZJBS series Low current start ZJB hold series
ZJS-Delay Series ZJS-Delay Series ZJS Delay Series ZJL Series (Current Type) ZJY(L) Series
ZJY(L) series ZJY-series ZJY series (voltage type) GBZ anti-jump intermediate relay
The above models are for reference only
3. The function and working principle of the intermediate relay 1. Isolation. The output signal of the control system is electrically isolated from the load terminal;
2. Conversion. For example, the output signal of the control system is, but the load uses power supply, and the input is reversible;
3. "Zoom in". The load capacity of the signal output by the controller is often limited, at the level of mA or several A, if there is a load that requires a larger current, it can only be converted through an intermediate relay;
4. Easy to maintain. Even if the output end meets the load current requirements, because it is integrated inside the controller, if it is damaged, it will be troublesome to replace and repair, but if it passes through the intermediate relay, the load on the output end is only the coil of the relay, which reduces the load on the output stage of the controller, thus Reduce the chance of damage. And when the intermediate relay contact is damaged due to frequent use, it is easy to replace it by simply plugging and unplugging.
working principle:
The coil of the intermediate relay is installed on the u-shaped magnetizer, and there is an armature on the magnetizer, and two rows of contact pieces are installed on both sides of the magnetizer, and the armature is lifted up in the non-moving state, so that the armature and the magnetizer Keep a certain gap between them. When the electromagnetic torque between the air gap exceeds the reaction torque, the armature is attracted to the guide magnet, and at the same time, the armature presses the contact shrapnel, so that the normally closed contact is opened and the normally open contact is closed. You have completed the signal. transfer.